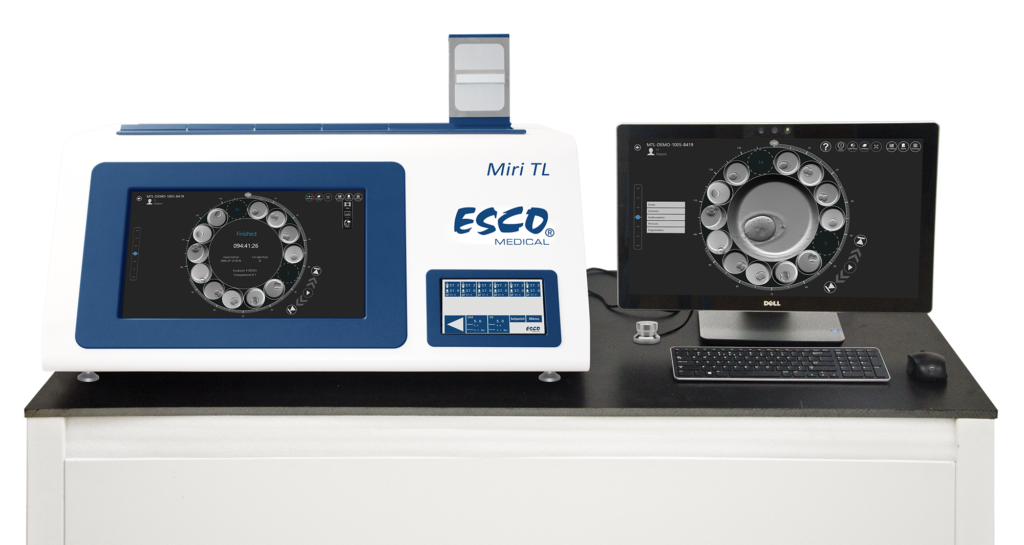
The MIRI® Time-Lapse Incubator
Is a multiroom incubator with a built-in camera and microscope. Designed and manufactured in EU, the MIRI® Time-Lapse Incubator provides high quality time-lapse images of embryos developing in “real-time” without having to remove the embryos from the safety of the incubation chamber for manual microscopy. Time-lapse embryo monitoring provides detailed morphokinetic data throughout embryo development, which is not available on routine spot microscopic evaluation. This allows all important events to be observed, helping to identify healthy embryos with the highest probability of implantation, with the aim of achieving higher pregnancy rates.
Time-Lapse Monitoring
6 (TL6) / 12 (TL12) independent chambers with precise temperature and gas regulation: Opening any chamber does not affect the environment in other chambers.

Heated Lid
Time-lapse video generated from images allows objective and reliable scoring and annotation of embryos for better prediction of future developmental.
Time-lapse Technology: Addressing IVF Risks
Time-lapse technology is a current system for the culture and imaging of embryos in vitro in the practice of Clinical Embryology. Risks associated with In Vitro fertilization (IVF) like multiple pregnancies and the related mother and neonate death rate has increased the past few years.
While more stringent policies on embryo transfer have eradicated some of these risks, the impact on the occurrence of twins remains to be a concern. It is said that a twin gestation can be evaded through a single embryo transfer only. Conversely, the conventional way of selecting the embryo’s morphology is not sufficiently and effectively analytical and predictive to permit routine single transfer of embryo; hence, novel screening tools are necessary.
Through the use of a time-lapse incubator, a continuous, non-invasive way of monitoring embryos is possible without the removal of the embryo from maintained, optimum culture conditions. With this, an IVF practitioner is able to observe information concerning cleavage patterns, morphologic deviations, and the dynamics of embryo development.